If you’re one of the many manufacturers who handle sulfuric acid, you know how important it is to store it safely. Mishandling this highly corrosive chemical could cause severe damage to your workforce and to your surrounding environment. But with so many variables to consider, where do you even begin to research sulfuric acid storage solutions? Whether you’re already familiar with storing sulfuric acid or you’re just getting acquainted with the chemical, you’ll save yourself hundreds of hours and thousands of dollars in sulfuric acid storage mistakes by reading this guide.
What is sulfuric acid?
Sulfuric acid is a highly corrosive mineral acid that challenges traditional chemical storage options. This pungent, colorless to slightly yellow viscous liquid is dyed dark brown during production to alert people to its hazards. The biggest challenge in working with sulfuric acid is that it is an aggressive oxidizer. This challenges the strength and design of many storage tanks. Poly Processing Company’s tanks and fittings can be combined specifically to store sulfuric acid and reduce the risks.

Challenges
Any company that stores sulfuric acid needs to be acutely aware of the dangers that the chemical presents to your equipment and your personnel.

Sulfuric acid poses the following serious storage challenges:
- Sulfuric acid is extremely heavy and will test the mechanical integrity of your storage tank. The inherent weight of sulfuric acid requires a strong material that can withstand the static load pressure constantly pressing against the bottom third of the storage tank.
- Sulfuric acid is an aggressive oxidizer. You must take appropriate safeguards to prevent the tank’s material from degrading, becoming brittle, and cracking—which could result in leaks or tank failure.
- If sulfuric acid makes contact with water, it creates a toxic sulfuric acid aerosol fume or a potential explosion.
- Sulfuric acid can create a highly flammable hydrogen gas if it is spilled on metals.
- Skin and other bodily burns from sulfuric acid can be more serious than burns from other strong acids. Sulfuric acid dehydrates whatever it touches, and the heat caused by that reaction with water can create secondary thermal damage.
Additional Resources:
Options
When considering storage solutions for chemicals like sulfuric acid, three available options are:
- Steel
- Fiberglass reinforced plastic (FRP)
- Polyethylene or cross-linked polyethylene.
Steel tanks are good for storing 98% sulfuric acid. At any other concentrations, it will need to be protected with some form of internal lining/liner. A rotationally molded polyethylene lining system is designed to protect your steel tank against the harshest chemicals to give you broad chemical resistance alongside the durability and strength of a steel tank.
FRP tanks are available with numerous interior coatings and a structural layer comprised of chopped glass fiber and resin.
Polyethylene or plastic storage tanks are either linear polyethylene or high-density crosslinked polyethylene. High-density crosslinked polyethylene, or XLPE, is a thermoset resin. It’s specifically engineered for critical applications like chemical storage.
Additional Resources:
Considerations
Some storage tank manufacturers are willing to provide 12,000-gallon linear sulfuric acid tanks. But time and experience have taught us that this isn’t the safest or most durable solution.
Some chemical companies will install large fiberglass tanks because they want to hold a railcar of sulfuric acid. While this may seem to be a convenient or cost-efficient solution, oftentimes it is the polar opposite. After losing 40,000 gallons of sulfuric acid in an instant, one manufacturer came to us to make the switch from a large fiberglass tank to a smaller one.
Under certain circumstances, you may be able to safely use larger tanks, but you should talk to your storage providers before making any commitments. At Poly Processing, we help you think through your chemical storage plans and make the best choice for your specific needs. Here are some things to consider when exploring different sulfuric acid storage tanks:
1. CHEMICAL COMPATIBILITY
Because it is an aggressive oxidizer, and reacts differently with various materials, choosing the right tank material is critical. You also have to consider it’s concentration since it displays different properties depending upon the concentration being used. For example, at 80% the nature of the chemical in this concentration does not have the same oxidizing effects. The three main concentrations are 93-98%, 80- 92%, and 80%.
2. CHEMICAL WEIGHT
At different concentrations, chemical weight also becomes a factor. At its highest concentration, its chemical weight is up to 16 pounds per gallon, nearly twice the weight of water. This should be stored in a tank that has a 2.2 specific gravity wall thickness and will test the mechanical integrity of any material.
3. ANTIOXIDANT SYSTEM
When storing sulfuric acid, it’s important to verify the hoop stress rating and understand the specific gravity ratings to make sure the resins used in the storage tank provide a margin of safety. Poly Processing Company’s next generation OR-1000™ system bonds the XLPE with an antioxidant inner surface, minimizing oxidation, reducing the potential for fault and maximizing lifespan.
4. SECONDARY CONTAINMENT
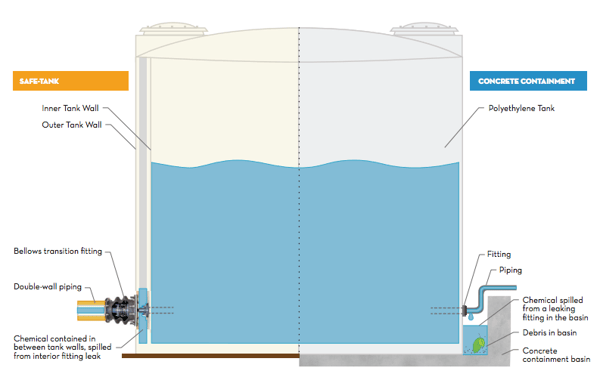
Secondary containment helps mitigate the risks and hazards associated with chemical spills and leaks. In this system, a secondary container or wall encompasses the primary container. Should the primary container fail and cause a chemical leak, the secondary container prevents the chemical from spilling outside the system. If secondary containment is needed, the Poly Processing Company’s SAFE-Tank® is a smart choice. If secondary containment is already present, the IMFO® tank is recommended because the tank’s structural integrity is maximized while providing a molded-in full drain fitting at the lowest point of the tank sidewall. When combining this tank design with the OR-1000™ system, oxidation is reduced dramatically.
Additional Resources:
Maintenance
Temperature
The temperature of the chemicals in your tank is very important. Check the temperature of your polyethylene tank regularly to verify that it never exceeds 100 degrees Fahrenheit. If you know that your tank will be subject to extreme temperatures, a specially-designed tank with a thicker construction is required. Avoid mixing or cutting chemicals in the same tank if the temperature will be negatively affected as part of the process. If you do mix chemicals that will affect the temperature, make sure the mixture is handled correctly (especially when dealing with higher concentrations and dilutions) and always check that the proper storing temperatures are met afterward.
Inspections
Certain annual inspections should be performed to ensure that your tank is maintained properly. Make sure you're cleaning your tank annually and inspecting it visually with a flashlight, looking for any abnormalities.
If you're not sure what to look for when inspecting your polyethylene tank, we can help. Our field service specialists have cameras and other specialized equipment -- as well as the expertise — to make sure everything is functioning the way it should.
Performing inspections on the original installation, checking the chemical storage temperature, and conducting regular annual inspections will help your polyethylene tank reach its maximum lifespan and ensure that it is properly maintained at all times. Tank Maintenance and Annual Inspection checklists can be found in the back of the Installation and Operation Guide
Regular tank inspections can reduce the expenses the tank owner may encounter on extending the life of the tank beyond 15+ years. Contact the Field Service team to learn more about our tank inspection service.
Additional Resources:
Installation
Proper installation is one of the first steps to a successful and long-lasting operation. The first thing our customer service team recommends is to examine the tank site. The installation site should be inspected to ensure the tank is properly installed according to industry standards. Sidewall fittings, venting, and proper bracketing are inspected to make sure the risk of tank failure is minimized, and the tank’s useful life is optimized. Many customers wish to avoid pipe support sidewall penetrations and design their own supports, which require inspection.
Make sure you have a smooth concrete, asphalt or steel foundation to accommodate IMFO®, SAFE-Tank® or vertical tank.
Additional Resources:
Build Your Solution
Proper tank design is crucial to successful and safe sulfuric acid storage. There are many many storage solutions out there which is why it is vital to choose the proper tank configuration. Selecting the right tank configuration can impact the safety of your employees, the protection of your environment, and the cost of protecting your investment.
Many people think that if a tank can store water, it can store a chemical. Although a water tank could potentially store a chemical for a limited amount of time, its design falls short of preventing leaks and other dangerous situations.
Don’t rely on your water tank to do the job of a tank designed for sulfuric acid storage. This is unwise and could cost you irreparable damage to your business. Instead, work with tank experts that can help you choose or design the right solution for your business.
For additional information on tank specifications for sulfuric acid storage download the Poly Processing Position Statement.
How can we help?
If you have any questions or would like to speak to a chemical storage expert, please submit a message using the form to the right. Our goal is to make sure you have all of the information you need to build a safe storage system for your specific application.
